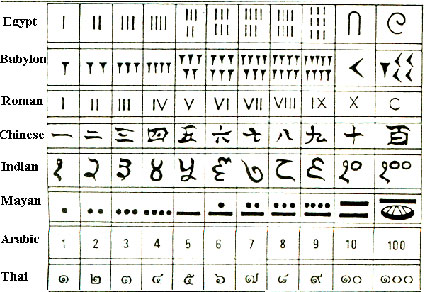
To answer the question «What is a numeral system?» also called system of numeration or base X (where X is a number) we will start with its definition. A numbering system is a set of symbols and generation rules that allow us to construct all valid numbers.
Mathematically it is expressed as: $$N = (S, R)$$ where:
- N: is the numbering system under consideration.
- S: is the set of symbols allowed in the system.
- R: are the rules that tell us which numbers and which operations are valid in the system.
They are classified into two main groups: positional and non-positional:
- In positional systems the value of a digit depends both on the symbol used, and on the position that symbol occupies in the number. This is the case of Roman numerals (I, II, III, IV, V, VI, VII…).
- In non-positional systems the digits have the value of the symbol used, which does not depend on the position (column) they occupy in the number. For example, modern Arabic numerals.
Note: both Arabic and Roman numerals are decimal system numbers (base ten).
The numbering systems are the basis for counting things, the material or in general the quantitative. However to count it is not necessary to make use of numbers, animals can count, a shepherd dog knows if there are sheep missing in his flock or not and he does it using his vision. The basic way to count is by using the senses (sight, touch, hearing, taste or smell) interacting with objects, shapes, colors or smells. While at a more complex level would be to make use of mathematical calculation, using the numbering systems with their rules and corresponding numbers.
And what does a number mean or represent? Well, there are two ways of defining it:
- In abstract form, it is the fundamental element of number system (set provided with two operations that verify certain conditions related to the commutative, associative and distributive properties).
- Of concrete form, it represents a metric quantity or an ordinal number that occupies a position within an order of a given series.
Graphically the number is written by means of symbols defined by the numbering system, these symbols or graphemes are called digits, and if they are formed by a single character is called digit. For example 2048 is a digit of the Arabic numeral system, and its digits are two (2), zero (0), four (4), and eight (8). The numbers 0, 1, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4, 5, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 are digits since they consist of a single digit.
Throughout history most civilizations have used the base ten system, however some civilizations such as the Mayans or the Aztecs used a vigesimal system (base twenty).
“Nowadays, the Arabic system is the most widely used to represent numbers. They are called “Arabic” because the Hispano-Arabs of al-Andalus introduced them in Europe through their cultural action, although their invention originated in India. The world owes to Indian culture the momentous invention of the positional numbering system, as well as the discovery of 0 (zero), called śūnya (shuunia) or bindu in Sanskrit language, however the Maya also knew both 0 and positional numbering.” [[#Wikipedia bibliography | Citation 4]]
Instead there are many more systems in use than we might expect, there is binary (in computing), ternary (logical comparison and ternary computers), quaternary (in quantum computing), octal (computing), hexadecimal (in computers). The minutes and seconds that are repeated every 60 or the hours every 12, do not form a numbering system of their own since they make use of the decimal system. This is the application of modular arithmetic, in this case modulo 60 and modulo 12.
The Fundamental Theorem of Numeration states the general formula for constructing a number N, with a finite number of decimal places in a positional numbering system of base b, such that:

where:
- N : valid number in the numbering system.
- b : base of the numbering system, number of symbols allowed in the system.
- d: digit, any symbol allowed in the numbering system.
- n: number of digits of the integer part, including zero (0).
- k: number of digits of the decimal part.
| Posición | … | 2 | 1 | 0 | -1 | -2 | … |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Valor base | … | b² | b¹ | b⁰ | $$b^{-1}$$ | $$b^{-2}$$ | … |
| Dígito | … | d² | d¹ | d⁰ | $$d^{-2}$$ | $$d^{-2}$$ | … |
| Ej: decimal base | … | 100 | 10 | 1 | 0.1 | 0.01 | … |
In conclusion, mathematics is not invented, it is discovered as a method to express abstractly the changes in nature; what is invented is the method of expressing it, but not the content.